Asparagus aphyllus L.,Crataegus azarolus L., and Ephedra alata Decne.have been used in traditional Greco-Arab herbal medicine to treat various metabolic and inflammatory diseases. However, to our knowledge, no scientific evidences regarding their anti-inflammatory effects have been published yet.This study aimedto evaluate the antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties of Asparagus aphyllus L., Crataegus azarolus L., and Ephedra alata Decne.extracts using in vitro mono and co-culture systems. Methods: In the first phase of the current study we measured the total phenol, flavones and flavonol contents as well as the antioxidant activity using the DPPH scavenging assay, ABTS assay, and reducing power of the three plant extracts. In second phase, we used THP-1-derived macrophages as a monoculture and co-culture with hepatic cell line (HepG2) to assess the effects of the three plant extracts on the production of LPS induced pro-inflammatory (IL-6 and TNF - alpha) and anti-inflammatory (IL-10) cytokines. Results: All three extracts exhibit relatively high levels of phenolics, flavones and flavonols, which correlate with their antioxidant capacities. All three extracts were found to modulate the secretion levels of TNF - alpha, IL-6 and IL-10 at non-toxic concentrations as measured with MTT and LDH assays. Conclusion: Taken together, our results suggest that the traditional uses of these extracts as anti-inflammatory remedies may be mediated by their significant antioxidant capacity, inhibition of pro-inflammatory cytokines secretion concomitant with enhancement of anti-inflammatory cytokines secretion
Main navigation
- Main
-
About AAUP
Image
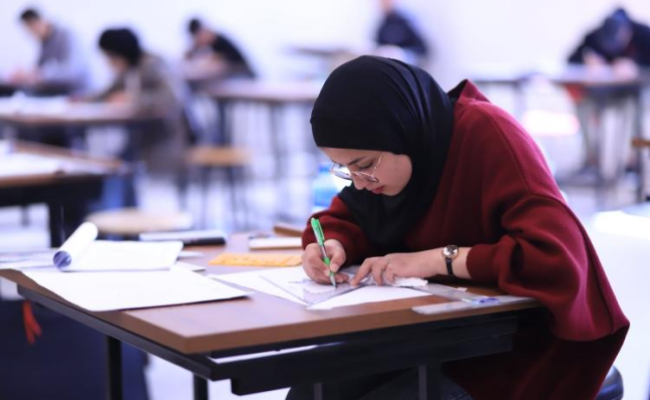


Give university
For those who wish to donate to the university, you can make your donations by filling out the donation form
-
Study
- Deanship of Admission and Registration
- Programs
- Prospective Student Admission
- Faculties
- Academic Quality
- Bridging to Bachelor's Degree
- Transfer to AAUP
- Visiting student
- Scholarships and Financial Aid
- Mobility and External Scholarships
- Tuition Fees and Costs
- E-Learning
- English Language Placement Test
Image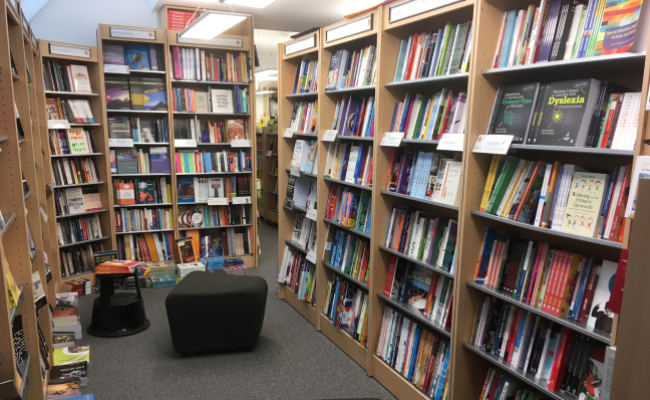

Arab American University Library
A distinguished library at the local and international levels by providing all electronic and paper information resources.
-
University life
Image
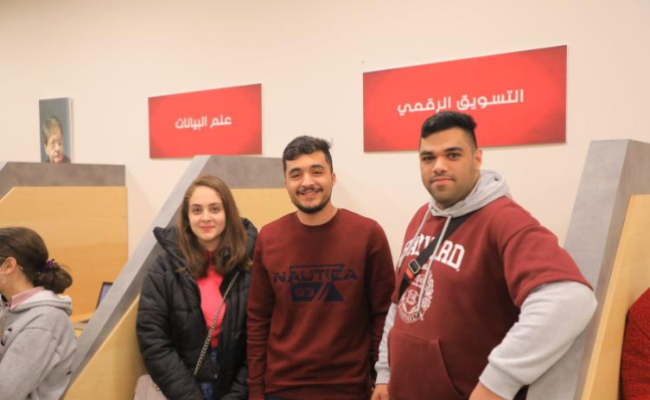

Inspiring success stories from the Arab American University
Success represents the pinnacle of persistence in the face of failure. So, these are the success stories we will share with you that reveal the path taken by some of our university’s graduates.
-
University centers
- Center for Research and Polling
- Climate Change Center
- Conflict Studies Research Center
- Continuing Education Center
- Dental Center
- E-Learning Center
- Hassib Sabbagh Center of Excellence
- Heart Center
- Language Center
- Medical Center - Ramallah
- National Digital Transformation and Artificial Intelligence Center
- Prosthetics and Orthotics Factory
- Simulation Center
Image
Medical Rehabilitation Complex
-
Research
Image


Arab American University Awards
As part of the university’s efforts to support and encourage scientific research, there are a set of awards to encourage researchers to excel in their original and valuable scientific production
-
Media Center
Image


AAUP ACADEMIC CALENDAR
An agenda to show the the important dates such as semester dates, registration, exams, activities, events, and holidays.
