Hydroxypropyl methylcellulosein an aqueous solution upon heating tendsto undergo thermalgelation, where thepolymer chains form a network and precipitatefrom solution. This occurs at a temperature known asthermal gelationpoint. Polymer precipitationcauses a significant drop in the shear viscosity. This could be a disadvantage in a hot environment or in applications were heat is applied. In this work, a hydroxypropylmethyl cellulose (HPMC)was formed that undergoes thermal gelationwith no polymer precipitationand with enhanced rheological properties. The target HPMC was prepared from wood pulp withalow content of carboxymethyl groups. The produced hydroxypropyl methylcellulose(CMHPMC)derivativeshowed uniquephysical properties that are not achievable with typical hydroxypropyl methylcellulose.The thermal gelation temperature of an aqueous solution of CMHPMC wasincreasedfrom 55 °C for commercial HPMC to 85 °C forCMHPMC. Asubstitution level of carboxymethylationthat led to an HPMC witha thermal gelation and with no precipitationwas determined to bea 0.15of carboxyl groupsper anhydroglucose repeat unit.In addition, the carboxymethylatedpulp showed an enhanced reactivity towards etherification reactions
Main navigation
- Main
-
About AAUP
Image
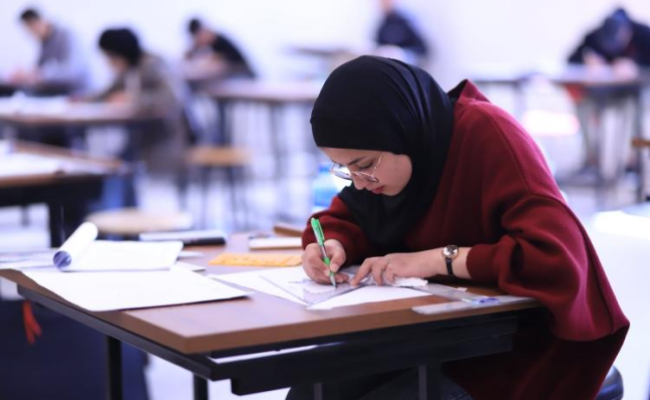


Give university
For those who wish to donate to the university, you can make your donations by filling out the donation form
-
Admissions & Academics
- Deanship of Admission and Registration
- Programs
- Prospective Student Admission
- Faculties
- Academic Quality
- Bridging to Bachelor's Degree
- Transfer to AAUP
- Visiting student
- Scholarships and Financial Aid
- Mobility and External Scholarships
- Tuition Fees and Costs
- E-Learning
- English Language Placement Test
- Academic Schedule
Image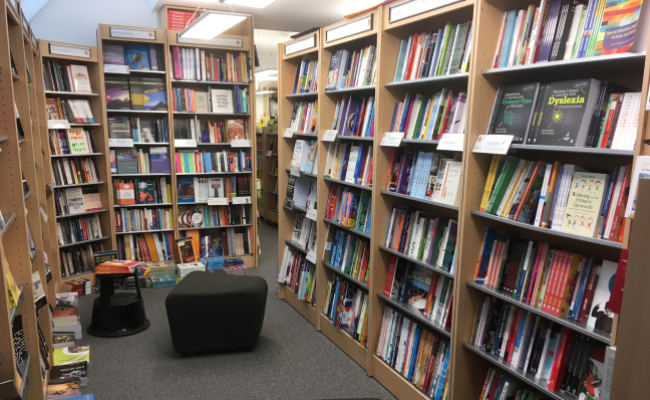

Arab American University Library
A distinguished library at the local and international levels by providing all electronic and paper information resources.
-
University life
Image
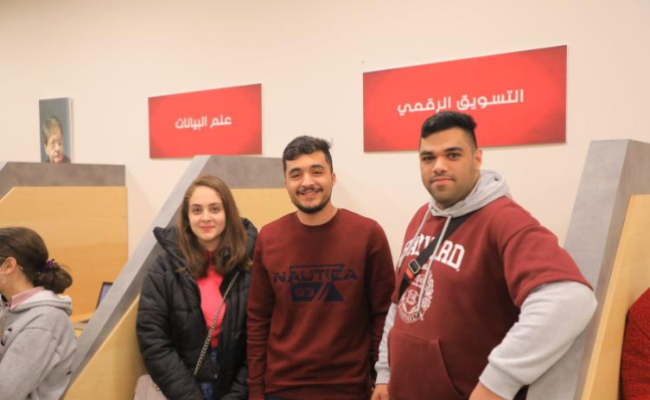

Inspiring success stories from the Arab American University
Success represents the pinnacle of persistence in the face of failure. So, these are the success stories we will share with you that reveal the path taken by some of our university’s graduates.
-
University centers
- Center for Research and Polling
- Climate Change Center
- Conflict Studies Research Center
- Continuing Education Center
- Dental Center
- E-Learning Center
- Hassib Sabbagh Center of Excellence
- Heart Center
- Language Center
- Medical Center - Ramallah
- National Digital Transformation and Artificial Intelligence Center
- Prosthetics and Orthotics Factory
- Simulation Center
Image
Medical Rehabilitation Complex
-
Research
Image


Arab American University Awards
As part of the university’s efforts to support and encourage scientific research, there are a set of awards to encourage researchers to excel in their original and valuable scientific production
-
News & Media
Image


AAUP ACADEMIC CALENDAR
An agenda to show the the important dates such as semester dates, registration, exams, activities, events, and holidays.
