Tetra(-4-pyridyl)porphyrinatomanganese(III)sulfate (as an MnIII+MnII ion mixture) was embedded into a polysiloxane polymer matrix and attached to the surfaces of the n-GaAs electrode. The n-GaAs/polymer/MnP system was annealed under nitrogen and used for a photoelectrochemical study in a water/LiClO4/Fe(CN)63−/Fe(CN)64− system. The values of short-circuit currents, measured after minutes of illumination, were significantly enhanced by modification. The modified electrode surfaces were more stable to degradation, in the dark and under illumination, than the unmodified ones. Furthermore, the modified electrodes showed higher light-to-electricity conversion efficiency than the unmodified ones. The methodology described here is advantageous in the sense that the semiconductor electrode properties can be enhanced in more than one aspect at the same time.
Main navigation
- Main
-
About AAUP
Image
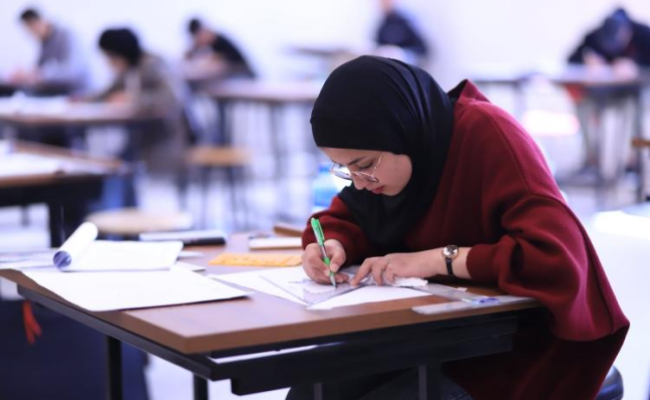


Give university
For those who wish to donate to the university, you can make your donations by filling out the donation form
-
Admissions & Academics
- Deanship of Admission and Registration
- Programs
- Prospective Student Admission
- Faculties
- Academic Quality
- Bridging to Bachelor's Degree
- Transfer to AAUP
- Visiting student
- Scholarships and Financial Aid
- Mobility and External Scholarships
- Tuition Fees and Costs
- E-Learning
- English Language Placement Test
- Academic Schedule
Image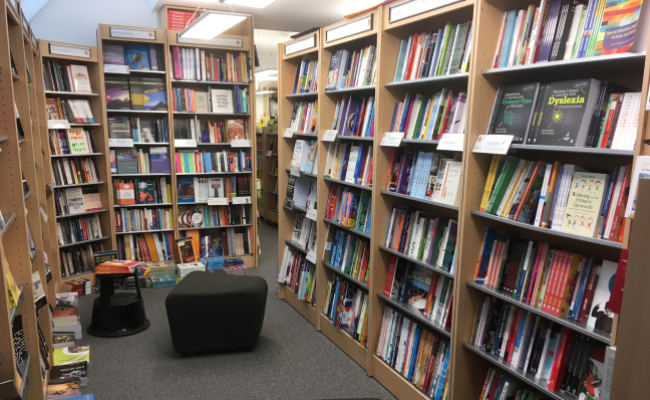

Arab American University Library
A distinguished library at the local and international levels by providing all electronic and paper information resources.
-
University life
Image
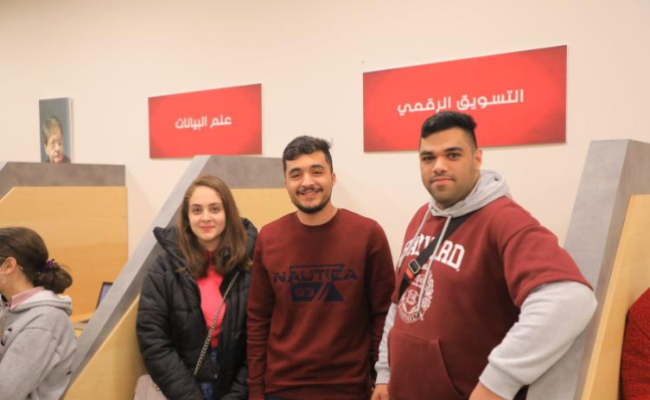

Inspiring success stories from the Arab American University
Success represents the pinnacle of persistence in the face of failure. So, these are the success stories we will share with you that reveal the path taken by some of our university’s graduates.
-
University centers
- Center for Research and Polling
- Climate Change Center
- Conflict Studies Research Center
- Continuing Education Center
- Dental Center
- E-Learning Center
- Hassib Sabbagh Center of Excellence
- Heart Center
- Language Center
- Medical Center - Ramallah
- National Digital Transformation and Artificial Intelligence Center
- Prosthetics and Orthotics Factory
- Simulation Center
Image
Medical Rehabilitation Complex
-
Research
Image


Arab American University Awards
As part of the university’s efforts to support and encourage scientific research, there are a set of awards to encourage researchers to excel in their original and valuable scientific production
-
News & Media
Image


AAUP ACADEMIC CALENDAR
An agenda to show the the important dates such as semester dates, registration, exams, activities, events, and holidays.
